 Campaign poster of Tsai Ing-wen and her running mate, Chen Chien-jen, in Datong District in Taipei, January 2016.
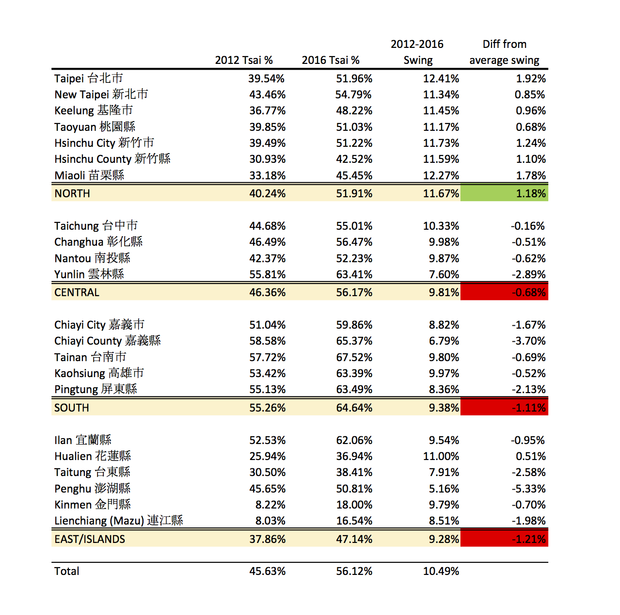
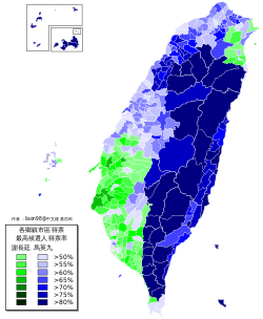
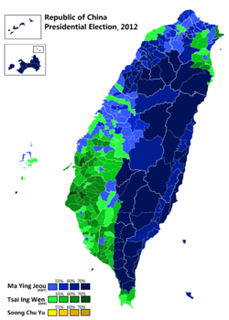
Campaign poster of Tsai Ing-wen and her running mate, Chen Chien-jen, in Datong District in Taipei, January 2016. Nationally, she won 45.63% of the total vote in 2012, and 56.12% in 2016, for a net aggregate swing of 10.49%. But this increase wasn't uniform across Taiwan. Her worst performance relative to 2012 was in Penghu, where her vote share increased from 45.65% to 50.81%, for a net swing of only 5.16%. Her best was in Taipei, where she increased her vote share from 39.54% to 51.96%, for a net swing of 12.41%, which gave her an absolute majority of the vote. Again, that was in Taipei, which was supposed to be the bluest stronghold of them all, and the most resistant to the appeal of the DPP ticket! (Or at least that's what this idiot thought.)
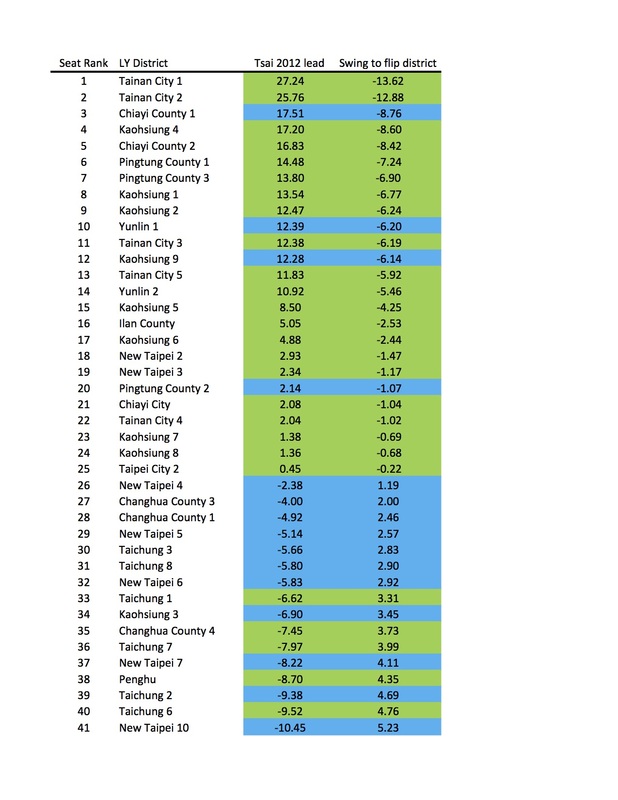
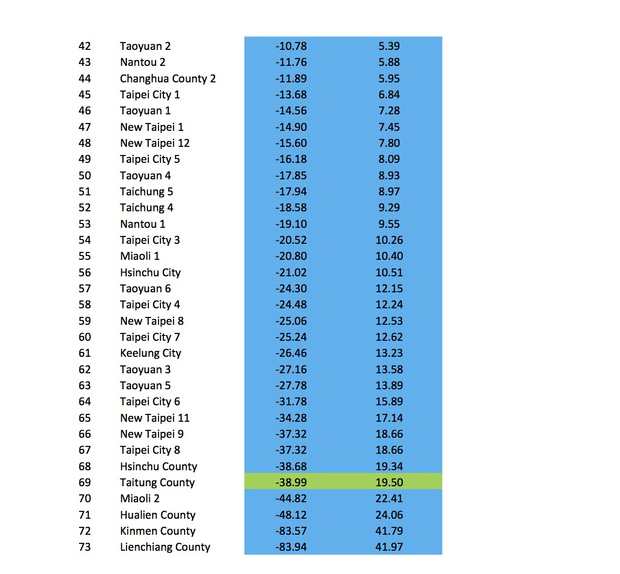
Moreover, Taipei wasn't an outlier. From Keelung all the way through Miaoli, Tsai's vote share increased more in every single northern jurisdiction than it did nationally, as the table below shows. By contrast, the swing toward Tsai was lowest in the south and east/island jurisdictions. And central Taiwan, where I thought the swing would be largest, was actually slightly behind the national average. (Perhaps that's one of the reasons several endangered KMT incumbent legislators in Taichung and Nantou held on to win re-election. More on that in another post.)
| 2016_post-election_swing_analysis.public.xlsx |
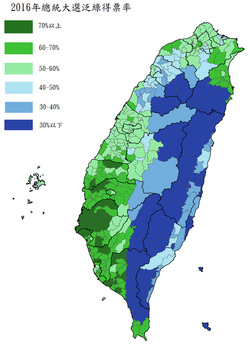 Taiwan 2016 presidential election results by township: not a blue north anymore.
Taiwan 2016 presidential election results by township: not a blue north anymore. Tsai's wins in the north are also surprising because the conventional wisdom has long held that Taiwan has a strong regional divide, with a deep blue north, deep green south, and swing districts in the middle. This is obviously a simplification, but it's so widely accepted among the political commentariat in Taiwan that there's even a wikipedia entry in Chinese for the phrase, "blue north, green south" (beilan, nanlü 北藍南綠).
The accepted explanation for these regional political differences is that they reflect socioeconomic and sub-ethnic ones: there are more waishengren in the north and east, aborigines in the east and central highlands, and a concentration of Hakka voters in Miaoli and Hsinchu Counties who have tended to support pan-blue candidates, while the Hoklo benshengren heartland of Tainan has been the DPP's strongest area.
But some research has found region to be a significant independent predictor of vote choice even accounting for partisanship, national identity, age, occupation, attitudes toward cross-Strait relations, and so forth. Why would this be? Part is probably a "local hero" effect--national candidates do better than average in their hometowns because of their long-standing personal connections there that trump partisan affinities. Part is certainly a factional story: when local factions switch sides they can bring a big chunk of votes with them all the way up to the presidential level. But while these effects certainly have existed in local and legislative elections for a long time, it's not obvious that they consistently matter in presidential ones.
Does Political Geography Still Matter in Taiwan?
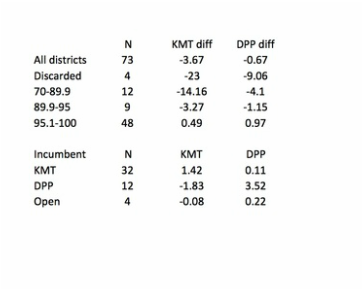
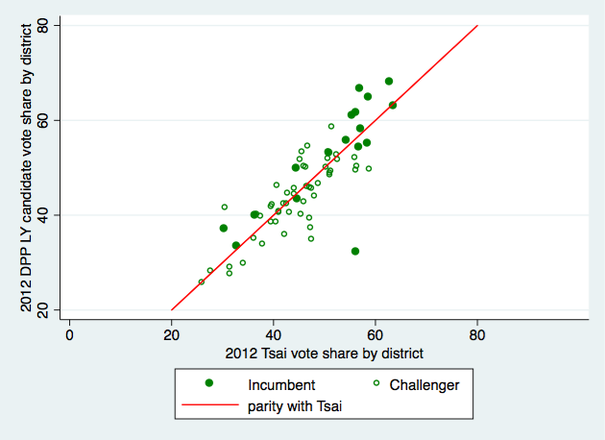
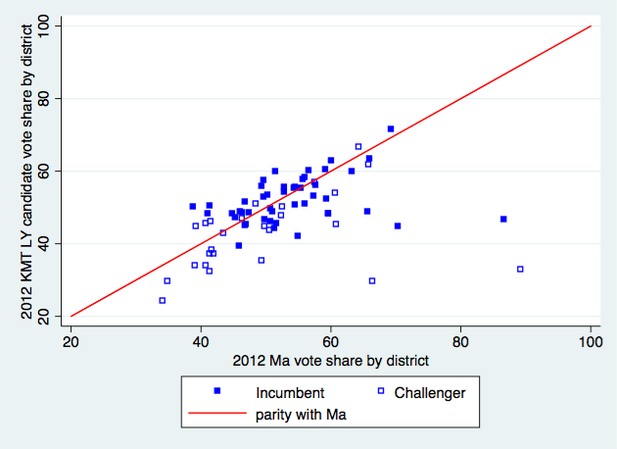
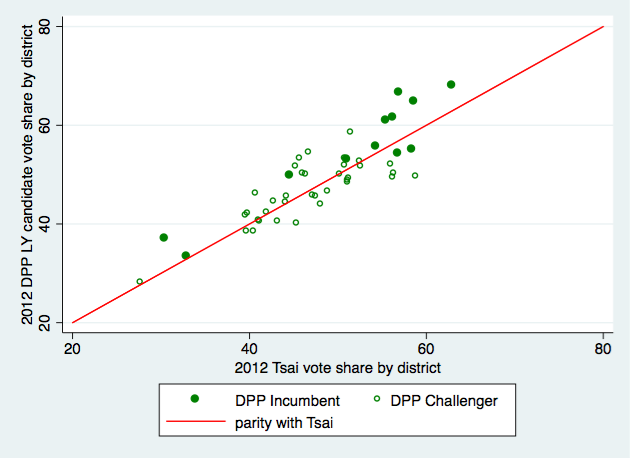
The way that Tsai won in 2016 leads me to think we should reconsider how, or even whether, geography has an independent effect in presidential elections. It's not self-evident that presidential vote choice in 2016 had anything to do with where voters lived, once we take into account all the usual demographic variables. There was no pan-blue firewall north of the Choshui River, and the DPP's win was clearly not built on turning out more core supporters in pan-green strongholds in the south. Instead, the swing data suggest a shift in the same groups of voters toward Tsai and away from the KMT all over the island. (Voting for the legislature is a different matter--I'll tackle that in a separate post.)
Granted, the swing toward Tsai was not as uniform as in 2012, when it ranged between only 2.58 and 4.88%. But still, in every single locality Tsai won at least 5% more in 2016 than she did four years ago. That suggests, for at least the last two elections, voters who switched their votes to Tsai did so because of factors not correlated with where they lived.
The best illustration of the irrelevance of geography to vote choice is what happened in New Taipei, where Eric Chu was, and still is, the mayor. He was re-elected there in 2014, holding on during a green wave that flipped most of the other local executives to the DPP. If a candidate's local connections matter at all, then Chu probably should have been able to deliver a hometown bump. Yet a little over a year later he won only 1/3 of the vote in New Taipei, winning 250,000 votes less than he did in the mayor's race, a lower share than the 37.5% he got in Taipei City proper and only 2 points above his island-wide total. And as the figures above show, Tsai Ing-wen improved more in New Taipei than she did nationally--not the result we'd expect if Chu was enjoying some kind of home-court advantage.
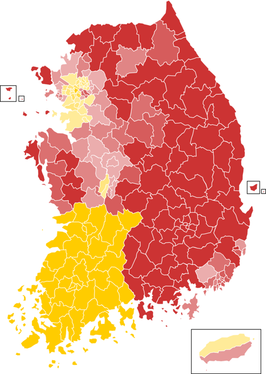 Regional voting patterns in South Korea: Jeolla in the southwest, Gyeongnam in the southeast.
Regional voting patterns in South Korea: Jeolla in the southwest, Gyeongnam in the southeast. Finally, consider the comparative angle. There's a country not far away that demonstrates exceptionally strong regional effects on voting behavior: South Korea. In the last presidential election there (in 2012), the opposition candidate Moon Jae-in won at least 85% of the vote in the three provinces that make up the southwest region of Jeolla, while the incumbent party candidate Park Geun-hye won over 80% in two provinces in the southeast region of Gyeongsang. That is a stark regional divide that has been present since the beginning of the democratic era in Korea. By this standard, Taiwan doesn't look very divided by geography at all.
Does Where You Live Affect Who You Support for President?
In fact, it's worth considering whether the "blue north, green south" trope has outlived its usefulness as a guide to voting behavior in Taiwan. The Taiwanese media often writes election narratives that emphasize geography as the key to understanding voting patterns in presidential elections, with frequent discussion of "battleground regions" and "swing districts." And political scientists, too, routinely use the language of electoral geography to talk about presidential campaigns. (I'm guilty of this too. For other instances, see here, here, and for a kick, this wikileaks cable from AIT.)
But if you think about this a bit, it's an odd way to characterize voting for a single national office. Taiwan doesn't have an electoral college, so an extra vote for Tsai in Penghu is worth the same as one in Taipei, or Taichung, or Hualien, or anywhere else in Taiwan. When we talk about "swing regions" we are implicitly underemphasizing factors that don't vary much by location and playing up ones that do, like factional ties. And I'm starting to think those other, non-geographic factors are where the real story is at, particularly differences between age cohorts. Something to keep in mind as we pour over the post-election survey data.





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
