In contrast, this time around the election campaign cycle was rather quiet for months -- one might even say boring. The polls showed little movement after Hou and Lai were formally nominated in June. There was a spike in interest when Terry Gou (remember him?) registered for a signature drive to run as an independent. And there was another in the run-up to November 24, when the prospect of Blue-White KMT-TPP cooperation on a joint presidential ticket got real, and then the deal fell apart, and then all three candidates announced their VP nominees and Gou declined to run (and now, to endorse anyone -- he's completely dropped out of sight!) The last month has felt more amped up, but the policy rollouts, debates, late breaking scandals, and insults have all felt very...normal...for a Taiwan presidential election campaign. There's just not the same sense of existential threat or inspiration that we saw in 2020 or 2016.
On Cross-Strait and US-Taiwan relations, there really isn't much difference between the three presidential candidates. The distinctions between them are harder to parse out than they were in past elections. Hou has tacked the KMT to the center, especially on defense policy and relations with the U.S.; Lai promises to continue Tsai's approach and shake off the accusation he's deeper green than she is; and to the extent Ko can be pinned down at all he's tried to squeeze himself somewhere in the constricting space between the two, supporting the call for defense budget increases while also embracing the KMT's call to revive the Cross-Strait Services Trade Agreement (CSSTA) with Beijing.
The stakes look very different to international audiences. The gap between the general domestic vibe and the framing of this race in many international media outlets has become a chasm. Read the English-language press and the headlines framed this as the election that could change the world. Meanwhile, the reaction of young voters, especially, that we've talked to has been a collective shrug. All three candidates are flawed in their own ways, and even people from their own campaigns will admit it privately. Nor do most people expect fundamental changes to come about as a result of this election. Add it all up and it's a recipe for low turnout.
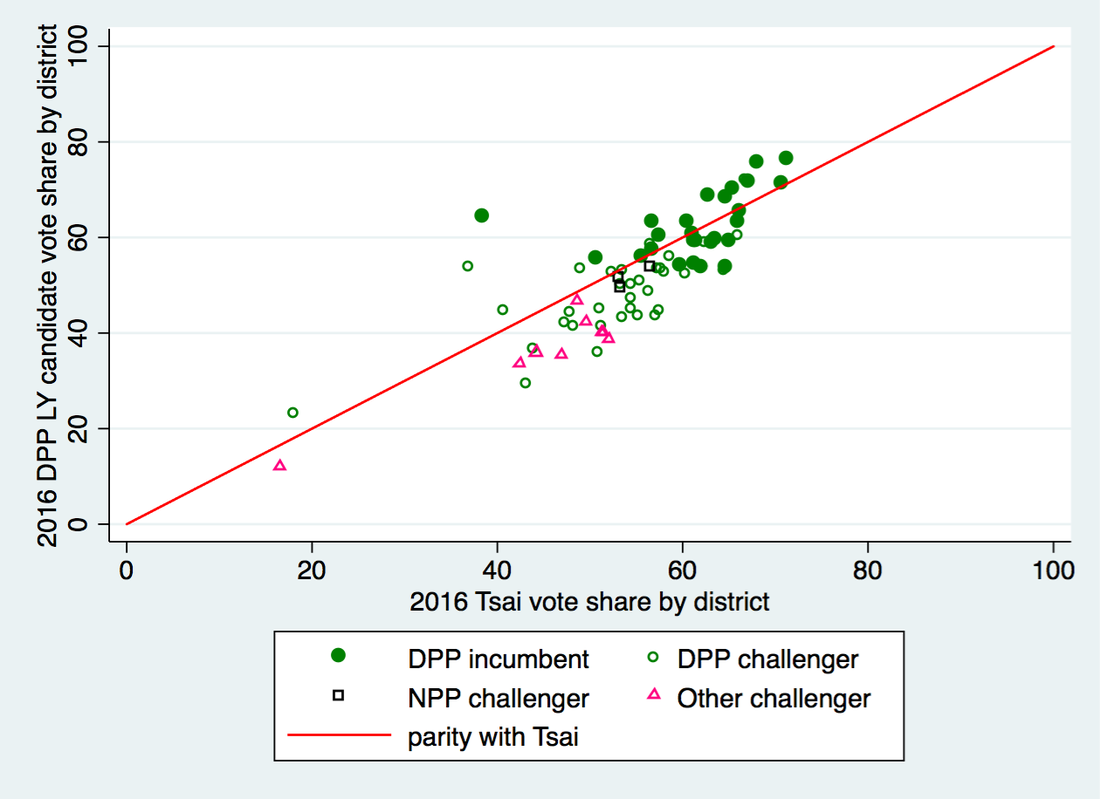
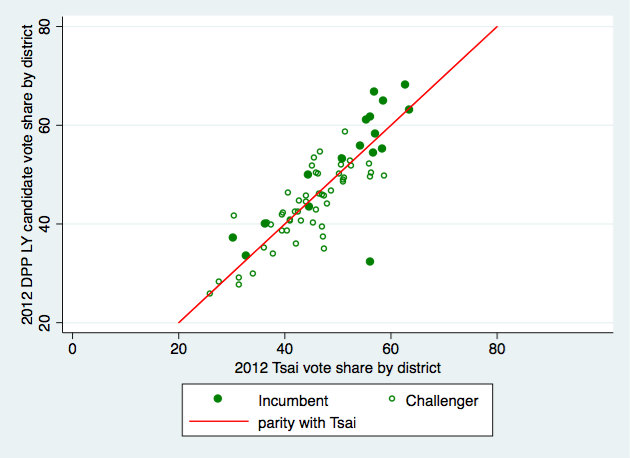
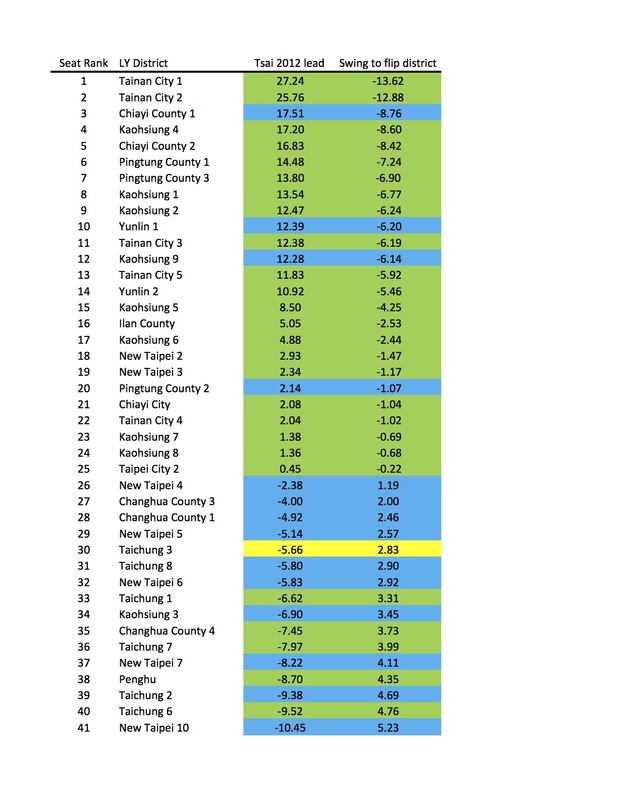
The legislative races are once again overshadowed, but quite important. The conventional wisdom we're heard is that the DPP will lose its majority -- it has 63 seats right now but is likely to lose at least 10, putting it below the 57/113 it needs. The KMT will be the main beneficiary -- possibly picking up 10 seats or more in the districts. And the TPP is likely to increase its seat share mostly via the party list vote -- last time it won five seats on 11.7% of the vote, and if it doubles that (23-4%) it would have 10 seats. The KMT has also yielded four districts to the TPP but they're all quite green, so I'd be surprised if the TPP has a single district legislator next month.
So, what we're looking at most likely is a split legislature, with both the DPP and KMT at roughly 48-53, and the TPP in the middle with 9-11. It's even possible that 2-5 independents could win and collectively be crucial to the legislative majority. Whoever wins the presidency is going to have to deal with multi-party politics and do coalition-building issue by issue in the LY.
Some Pre-Election Expectations

Turnout will be down. My prior here is that it will be close to the 2016 level, at say 66-69%. The weather is good but, again, subdued campaign with flawed candidates.
The TPP's party list vote will be close to Ko's vote share. For once, the party list, which is decided by voters' second vote, is potentially crucial to determining the balance of power in the LY. In the absence of other information I'm guessing the TPP's list will do about as well as Ko does in the presidential race.
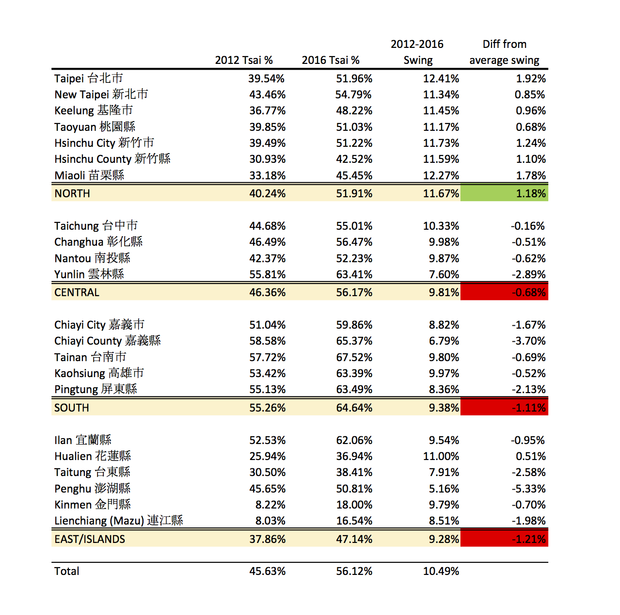
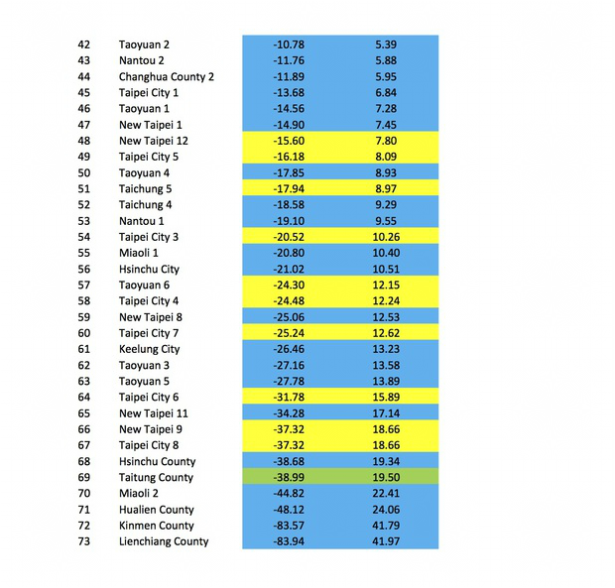
The KMT comes close but does not surpass the DPP as the largest party in the Legislative Yuan. The electoral system has a slight (2-5 seats) bias in favor of the KMT, and at this point I think we can say the party's candidates typically do better in the district races, where family legacy, constituent service, factional ties, and other things that localize voting patterns matter more than in the presidential election. Going through district by district, my best guess is that the KMT picks up a net of 5 seats in the greater Taipei area (Taipei, New Taipei, and Keelung [UPDATE: and Taoyuan]), holds in Hsinchu and Miaoli, nets 4 seats in central Taiwan (Taichung, Nantou, Changhua), and flips 2 elsewhere (Tainan, Kaohsiung, Pingtung, Taitung, Yilan, etc. [UPDATE: and Yunlin, Chiayi]) KMT candidates will probably also win back at least one of the two seats in the indigenous districts (1 highland, 1 lowland) that the DPP holds now. That would net the party 12 seats, putting them at 50. The DPP drop in this scenario is around the same which would put them at 51 seats.
It's also not fully appreciated how close they were in the PR list last election: the DPP won 34% and the KMT 33% there (both got 13 seats). If both parties are mostly relying on core supporters to cast a party vote, as they did last time, then I'd expect them to look similar again, maybe down a seat or two from 2020. Let's call it 1 seat down for each.
Add that up and we've got KMT 49, DPP 50, TPP 10, and others 4.
And finally...
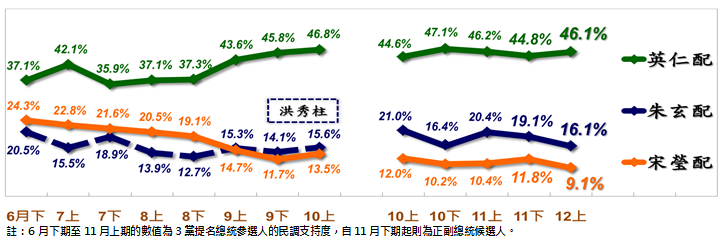
I think Lai wins the presidential race, but it's pretty close. He's been ahead in the polls all year, by a little to a lot; not one reliable polling company ever found Hou in the lead. I expected dissatisfaction with the DPP government to manifest in soft numbers for Lai, which it did -- he's rarely if ever broken 40% in polls over the last six months, and clear majorities support a change in ruling party in this election. But I also expected eventually anti-DPP voters would finally converge around Hou, and that doesn't appear to have happened. Instead they have remained divided on who they would prefer to see instead, and even on who is the strongest candidate (Ko or Hou) if they are to vote strategically. In the end this probably dooms Hou's chances of pulling the upset. Ko's enduring strength has surprised me, but his chances depend greatly on support from the most fickle potential voters: those in the youngest cohorts (below roughly 28yo), and I still expect him to finish a clear third.
With Ko soaking up a lot of the disaffected voters, and with both parties turning out their bases and not attracting much beyond, I expect the larger generic size of the green camp to be decisive. I'll predict: Lai wins with about 40%, Hou with 35%, and Ko with 25%. I'm not going to venture a guess about the final raw vote tallies but I will go out on a limb and predict Hou won't hit Han Kuo-yu's 5.5 million in 2020; and Lai will fall short of the 6 million mark that Tsai hit in all three of her campaigns.










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
